Scattered Spider Unveiled: Navigating the Web of Sophisticated Data Breaches
With over 100 organizations targeted, the rise of Scattered Spider underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.
The group targeting Business Process Operations (BPO) sectors has upped its game and now targets larger enterprises with huge data potential. They gain legitimate entry into your system, move around the network, and inspect the loopholes before going in for the kill.
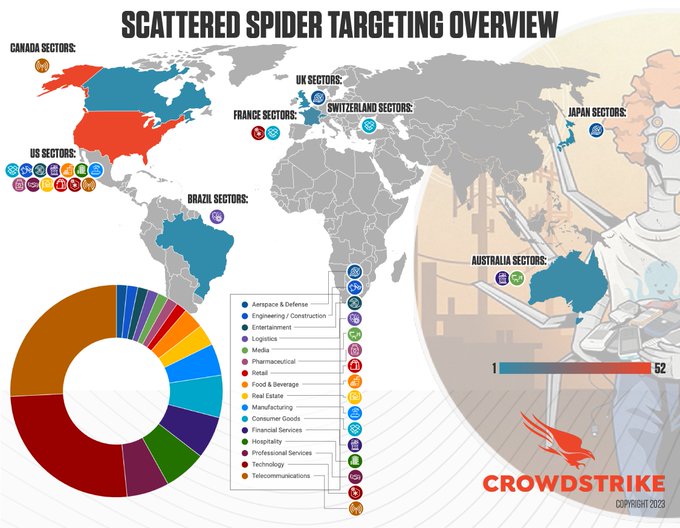
An interesting fact revealed by CrowdStrike’s infographic on Scattered Spiders Target overview is the similarity of the group with their namesake insect – the Spider. Akin to a spider with eight legs, the group is scattered across eight sectors around the globe.
Understanding the modus operandi of Scattered Spider is the first step towards fortifying your organization against such cybersecurity threats.
Let’s delve into who Scattered Spider is and what differentiates their data breaches from others.
Who is Scattered Spider?
Scattered Spider, also known as UNC3944, Scatter Swine, and Muddled Libra, is a financially motivated threat actor group.
They use tactics like phone-based social engineering and smishing attacks to gain authentic credentials of victims to launch their attacks. The group mainly comprises Europeans and individuals from the US in their teens and 20s as of September 2023. They gained notoriety and made a name for themselves in the Dark Web when they hacked – Caesars Entertainment and MGM Resorts International, two of the largest casino and gambling companies in the United States.
Scattered Spider hackers are known to target environments that are widely used by various industries and sectors. In short, they target Windows, Linux, Google Workspace, AzureAD, M365, and AWS.
Peek into their Past
Founded in May 2022, Scattered Spider focused on attacking Telecommunications firms.
The group back then used SIM swapping, MFA fatigue attacks, SMS phishing (Smishing), and phishing via Telegram to launch their attacks. Scattered Spider exploits known security bugs, such as CVE-2015-2292, to bypass security measures – a cybersecurity issue in Windows’ anti-DoS software. It terminates security software and allows the group to evade detection.
With a deep understanding of Microsoft Azure, Scattered Spider can conduct investigations in cloud computing platforms that AWS and Google Workspace power. It uses remote-access tools that are legitimately developed, thus evading security alerts.
In mid-2023, the group gained notoriety when they targeted high-profile casinos, but before this, Scattered Spider was recognized for targeting critical infrastructure.
What is the Modus Operandi of Scattered Spider?
Their modus operandi is simple yet disastrous for an organization.
Being an expert in social engineering attacks, the group deploys attacks like
- SMS Phishing (Smishing)
- Voice Phishing (Vishing)
- Phishing using Telegram
- SIM Swapping
- MFA Fatigue
The group is renowned for its technique of impersonating IT or contractor personnel and stealing legitimate login credentials.
CrowdStrike conducted an investigation where it was revealed Scattered Spider hackers used compromised credentials of their victims. Once the Scattered Spider hackers are inside the network, they create Azure Virtual Machines (VMs), which are used to carry out activities involving credential (identity) theft. They use the following remote monitoring and management tools along with utilities to maintain their access.
Considering the tools mentioned are not malicious, they don’t signal alerts and can evade them.
Additionally, they are not blocked by endpoint detection and response (EDR) technology.
- DWservice
- Level.io
- AnyDesk
- Itarian Endpoint Manager
- BeAnywhere
- TrendMicro Basecamp
- Domotz
- Fixme.it
- Fleetdeck.io
- Logmein
- ManageEngine
- N-Able
- Pulseway
- Rport
- Rsocx
- ScreenConnect
- SSH RevShell and RDP Tunnelling via SSH
- Teamviewer
- Sorillus
- ZeroTier
Lastly, Scattered Spider hackers use tools below tools to terminate security software and evade detection.
- POORTRY is used to terminate selected Windows systems processes.
For instance, the group signed the POORTRY driver with a Microsoft Windows Hardware Compatibility Authenticode signature to evade detection.
- A Windows userland utility, STONESTOP, attempts to terminate processes.
It is done by creating a malicious driver and then loading it. STONESTOP is a loader and installer for POORTRY and an orchestrator to instruct the driver on what actions must be performed.
The Vulnerability Scattered Spider Hackers Exploit
Usually, Scattered Spider exploits CVE-2015-2291 with tools like STONESTOP and POORTRY.
CVE-2015-2291 is an Intel Ethernet diagnostics driver for Windows (iqvw64.sys) vulnerability.
It allows local users to cause either a denial of service or execute arbitrary code with kernel privileges through a crafted IOCTL call.
A scattered Spider exploits this CVE-2015-2291 vulnerability to deploy a malicious kernel driver in the Intel Ethernet diagnostics for Windows (iqvw64.sys).
The group has also exploited CVE-2021-35464.
It is a flaw in the ForgeRock AM server. The ForgeRock AM server versions before 7.0 have a Java deserialization vulnerability in the jato.pageSession parameter on multiple pages.
This vulnerability exploitation doesn’t require authentication. You can trigger the remote code execution by sending a single crafted request to the server.
But Why Does this Vulnerability Occur?
The vulnerability occurs because of the usage of Sun ONE Application Framework (JATO) found in Java 8 or earlier versions.
The group has exploited the CVE-2021-35464 vulnerability to run code and boost its privileges on the Apache Tomcat user on an AWS instance. Scattered Spider used a compromised AWS token to request and assume permissions for an instance role.
The group has showcased an in-depth understanding of the Azure environment and leverages built-in tools for their attacks.
Scattered Spider and Its Web of Data Breaches
Scattered Spider has been active since May 2022 and targets Telecom and Business Process Operations (BPO) organizations across eight sectors, including
- Canada
- US
- UK
- Australia
- Brazil
- France
- Switzerland
- Japan
Per the cybersecurity research group’s CrowdStrike 2023, Global Threat Report, Scattered Spider is known for stealing sensitive data and leveraging trusted organizational infrastructure for further attacks on downstream customers.
Initially, the Scattered Spider victims were from the Telecom and BPO sectors; however, in January 2023, Scattered Spider changed their tactic and became involved in over half a dozen incidents from mid-2022.
Large outsourcing firms that served high-value cryptocurrency institutions and individuals were targeted during this period.
Recently, they moved on from their traditional target sectors and made news with their attacks on two high-profile casinos, MGM Resorts and Ceasars in the US.
With the immense knowledge of European businesses, the group is highly focused on stealing large amounts of sensitive data for extortion.
Data Theft is the Primary Focus
The group is highly focused on stealing sensitive data from the victim’s legitimate account.
Personal Identification information theft is their primary focus as PII gives them undeterred access to the organization’s sensitive data, and they can steal the confidential data without creating a security alert.
As stated earlier, the group is focused on stealing the authentic credentials of employees and users to gain legitimate access to the organization’s network. While the Scattered Spider group is financially motivated, data theft is their primary focus. Reason:
The stolen data is used for further attacks on an organization; as it is legitimate data, it evades regular alerts.
Key Preventive Measures
Some of the critical preventive measures organizations must take to ensure a secure IT infrastructure are:
1. Regularly Update their Software
It is imperative to keep your software updated all the time you get an update alert. The alerts carry the patches that help protect your software against any vulnerability.
2. User Training and Guidance
It is essential for your organization to impart custom-made training and offer guidance to all users. It will avoid any human error on their part.
3. Antivirus and Antimalware
Invest in good antivirus and antimalware to protect against any viruses or malware threats.
4. Behavior Prevention on Endpoint
There should be security controls implemented at the Endpoint to identify and prevent the execution of any malicious files.
5. Application Isolation and Sandboxing
Any corrupted application should be isolated and sandboxed to prevent the malware from spreading across the network.
6. IAM Resilience
Having robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) resilience capabilities such as automated backup and recovery, continuous data verification, and Point-in-Time investigation and restoration is paramount.
Conclusion
Scattered Spider is an emerging threat to organizations with unpatched vulnerabilities and weak admin passwords. To protect your organization from threats of Scattered Spider, it is recommended to scrutinize every legitimate login activity and to get multi-factor authentication approvals from assets, locations, and accounts that are unexpected.
By leveraging Acsense’s comprehensive IAM resilience platform, you can significantly fortify your IAM systems against the nefarious tactics employed by groups like Scattered Spider.
Schedule a demo to learn how Acsense can help bullet-proof your cloud IAM and ensure rapid recovery.
FAQs:
1. What are the common signs and symptoms of a Scattered Spider data breach?
The Scattered Spider Group is an expert in evading detection. Here are some common indicators of ongoing data breaches:
- Sudden changes in files
- User accounts are locked
- Device speed goes down, and network performance is affected
- Your system behaves abnormally
- Unusual account activity
2. How can I protect sensitive customer information from Scattered Spider attacks?
You can protect your customers’ sensitive information through sandboxing.
It makes it difficult for intruders to advance their operations by exploiting undiscovered or unpatched vulnerabilities. Other types of virtualizations and application micro-segmentation may also mitigate the impact of some kinds of exploitation.
3. What are a Scattered Spider data breach’s potential legal and regulatory consequences?
The potential legal and regulatory consequences of a Scattered Spider data breach can lead to fines, penalties, and even lawsuits. It implies there will be additional expenditure over and above the cost of downtime and production, and not to forget the ransomware cost, should the group demand the same.
4. What steps should I take immediately after discovering a Scattered Spider data breach?
After a Scattered Spider data breach, the first step would be to isolate the infected device and the network to mitigate further damage. Mitigation steps should also involve limiting the installation of unapproved software.
5. What type of data is typically targeted in Scattered Spider data breaches?
Scattered Spider hackers are known to steal sensitive and confidential data from their victims.
The stolen data or credentials are then used for follow-on attacks on environments outside the victims’ proximity.
