The AWS outage of October 2025 exposed the limits of vendor responsibility. While hyperscalers restore their own infrastructure, IAM resilience ensures your identity tenant — Okta, Entra ID, or Ping — can recover quickly from failures that are your responsibility.
TL;DR
The AWS outage wasn’t about security failure — it was about dependency failure. When AWS went down, millions of services stopped because one provider controlled the backbone. The same dynamic exists inside your IAM stack: if your Okta or Entra tenant suffers a misconfiguration, ransomware, or deletion, your organization could face the same downtime — except this time, it’s your responsibility. IAM resilience bridges that gap.
Table of Contents
- 1. What Happened During the AWS Outage (October 2025)
- 2. Understanding Shared Responsibility in the Cloud
- 3. Hyperscaler vs. IDP vs. Customer IAM Responsibility
- 4. Why IAM Resilience Is a Business Continuity Requirement
- 5. Building a Resilient IAM Environment
- 6. Lessons for CISOs and IAM Leaders
- 7. Conclusion
1. What Happened During the AWS Outage (October 2025)
On October 20, 2025, AWS’s US-EAST-1 region experienced a multi-hour outage caused by DNS resolution issues affecting DynamoDB and load balancer endpoints, according to AWS’s official report.
This was a hyperscaler-level event: the kind of infrastructure failure no customer or third party can control. Apps like Reddit, Venmo, and Slack went down not because they were hacked, but because their dependency — AWS — was temporarily offline.
The incident wasn’t a security flaw. It was a resilience failure.
And it mirrors what would happen if your identity layer — Okta, Entra, or Ping — suffered an internal outage. When the system that controls access goes down, everything stops.
2. Understanding Shared Responsibility in the Cloud
Cloud computing operates on a shared responsibility model:
- Hyperscalers (AWS, Azure, GCP) are responsible for security of the cloud — physical infrastructure, power, networking, and hypervisor uptime.
- Customers are responsible for security in the cloud (your tenant) — data, configurations, access, and resilience of what they build on top.
Reference: AWS Shared Responsibility Model

When AWS has an outage, AWS fixes it.
When you have a tenant outage — an IAM failure, deletion, or lockout — you must fix it.
That’s the line too many organizations misunderstand until it’s too late.
3. Hyperscaler vs. IDP vs. Customer IAM Responsibility
Type of Outage | Example | Responsibility | Can Acsense Help? |
Hyperscaler outage | AWS region failure, DNS or load balancer issues | AWS, Azure, or GCP | ❌ No – infrastructure layer |
IDP vendor outage | Okta or Entra ID service downtime | Identity vendor | ❌ No – vendor layer |
Customer IAM outage | Misconfiguration, ransomware, human error, insider action | You (the customer) | ✅ Yes – Acsense’s IAM Resilience Platform |
Why This Distinction Matters
You can’t prevent AWS or Okta from going down.
But you can prevent a misconfiguration, deletion, or ransomware attack inside your own tenant from taking down your entire identity fabric.
That’s where IAM Resilience comes in — a discipline built for the customer side of the shared responsibility model.
4. Why IAM Resilience Is a Business Continuity Requirement
When your IAM system fails, it’s not just IT downtime — it’s business paralysis.
- Employees can’t authenticate.
- Applications can’t authorize.
- Security teams can’t investigate.
For organizations running on Okta, Entra ID, or Ping, the IAM tenant itself becomes a single point of failure.
Yet most companies still treat IAM backup and recovery as an afterthought — until an incident occurs.
Acsense was built to close this gap.
- Continuous IAM Backup: Immutable, versioned copies of every configuration, group, policy, and role.
- Safe Change Management: Ability to preview and test IAM changes before deploying them to production.
- Posture Intelligence: Continuous integrity checks to identify risky drifts and untested configurations.
- Rapid Recovery: Restore an entire IAM tenant — or a single object — in minutes, not days.
Learn more: Acsense IAM Resilience Platform
This is resilience at the identity layer — the layer that hyperscalers and IAM vendors alike don’t cover.
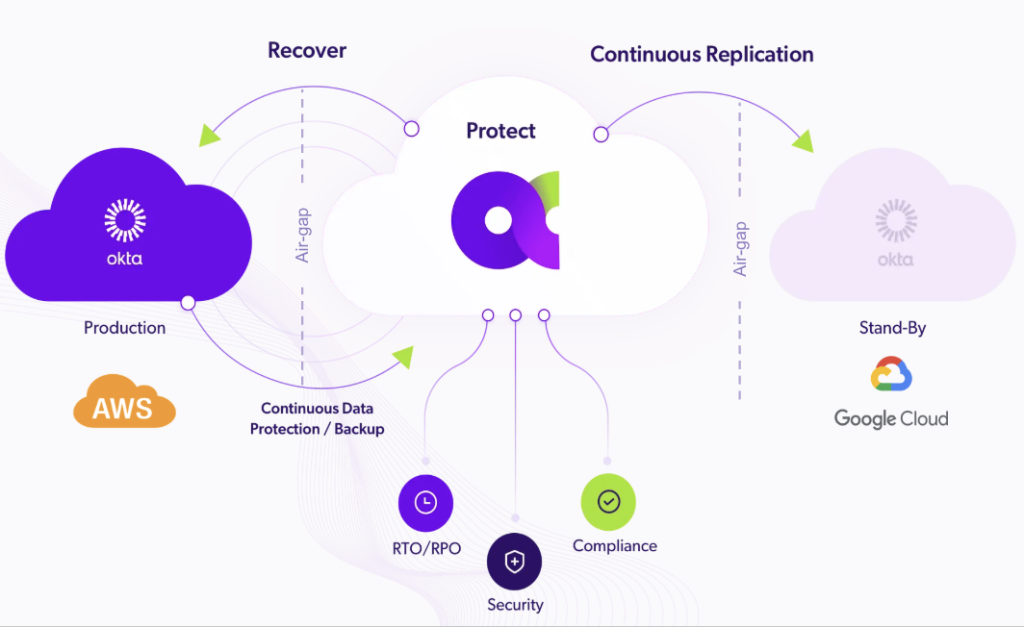
5. Building a Resilient IAM Environment
The goal is simple: if your tenant blinks, you don’t.
Here’s a pragmatic blueprint aligned to common frameworks and real‑world incident response. NIST Publications
1) Inventory Your Identity Control Plane
- Enumerate providers (IdP, PAM, IGA), regions/tenants, and integrations.
- Map critical objects: identities, groups, roles, policies, conditional access, MFA, app assignments, trust configs.
- Identify blast radius for each object.
- Tag tier‑0 auth paths and admin roles.
- Document dependencies (network, DNS, secrets, SCIM, HRIS, directories).
2) Back Up What Matters, Not Just Data
- Capture config + policy state, not only accounts.
- Keep immutable copies with retention and legal hold options.
- Support object‑level restore and bulk tenant rollback.
- Store backups in a separate trust boundary (air‑gapped or logically isolated).
3) Engineer For Recovery, Not Just Backup
- Define RTO/RPO per identity flow (user login, admin login, break‑glass).
- Build playbooks:
- “Revert broken MFA policy”
- “Restore deleted admin group”
- “Rollback SAML/OIDC config”
- “Recover app assignments for tier‑0 systems”
- “Revert broken MFA policy”
- Test partial and full‑tenant restore paths.
4) Protect The Protectors
- Guard backup access with least privilege, MFA, and segregation of duties.
- Monitor for suspicious change patterns and mass‑deletion events.
- Keep break‑glass credentials out‑of‑band and review quarterly.
5) Prove It Works (Audits, Assurances, Board)
- Run tabletop and live‑fire exercises.
- Record evidence of recoverability (screens, logs, timestamps).
- Report time‑to‑restore and config drift as board‑level metrics.
- Align with NIST CSF 2.0 outcomes and CISA incident‑response guidance. NIST Publications
Acsense POV: Our purpose is IAM resilience.
We don’t keep AWS up.
We keep you up when your IAM tenant is the problem—by making backups automatic, changes observable, and recovery fast and surgical.
Learn more about IAM Resilience
_______________________
Helpful internal resources:
- https://acsense.com/blog/iam-audit-assessment-4-questions-to-prove-compliance-resilience
- https://acsense.com/blog/okta-disaster-recovery-plan-a-practical-guide-for-2025
- https://acsense.com/blog/ransomware-backup-systems-protecting-idps-from-cyberattacks
- https://acsense.com/blog/why-test-your-identity-backups
6. Lessons for CISOs and IAM Leaders
- Outages are inevitable. Whether it’s AWS or Okta, no vendor offers zero downtime.
- Resilience is your responsibility. You can’t outsource your ability to recover.
- Compliance depends on recoverability. Regulations like NIS2 and DORA demand evidence of tested IAM continuity.
- Downtime costs scale with dependency. When identity stops, everything stops — authentication, authorization, audits.
Backup isn’t resilience.
True IAM Resilience means continuity, observability, and verified recovery — not just stored data.
7. Conclusion
The AWS outage of October 2025 was beyond anyone’s control — but it offers a clear warning.
When the infrastructure goes dark, recovery is the vendor’s job.
When your IAM tenant breaks, recovery is your job.
That’s the reality of the shared responsibility model — and the reason IAM Resilience has become a critical layer of modern security architecture.
Acsense doesn’t prevent outages. It ensures your identity systems recover fast, data stays intact, and your organization stays operational — no matter who or what caused the disruption.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can Acsense prevent an AWS outage?
No. Hyperscaler outages like AWS are vendor-side events that no customer or third party can control.
Acsense protects against customer-side IAM disruptions — such as misconfigurations, ransomware, or human error inside your Okta, Entra, or Ping tenant.
- What is IAM Resilience?
IAM Resilience is the ability to maintain identity and access continuity even when your configurations are corrupted, deleted, or attacked. It includes continuous backup, monitoring, and rapid recovery of IAM systems to minimize downtime and business disruption.
- How does IAM backup differ from vendor recovery?
Vendor recovery restores the platform’s availability (e.g., Okta or Entra ID coming back online).
IAM backup restores your tenant’s specific configuration and access data — your groups, policies, app assignments, and conditional access settings. That’s your side of the shared responsibility model.
- What frameworks cover IAM continuity?
Frameworks like NIST CSF 2.0, and regulations including DORA, NIS2, and APRA CPS 230, all require tested recovery and operational continuity for identity systems.
- Why does this matter to CISOs and executives?
Because IAM downtime equals business downtime.
When access breaks, employees can’t log in, customers can’t transact, and compliance obligations are jeopardized. IAM Resilience protects operations, brand trust, and audit readiness.
